AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perform tasks, make decisions, and interact independently with users or systems. Powered by machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and advanced algorithms, these agents interpret user input, analyze data, and execute actions with precision. Unlike static tools, AI agents learn and adapt, improving efficiency over time.
Adaptability is their core strength. They process data, detect patterns, and deliver context-aware responses. For example, virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa offer personalized services, while customer support chatbots ensure prompt and effective communication.
AI agents are pivotal in industries like healthcare, customer service, and e-commerce. They streamline operations, optimize workflows, and enhance user engagement, delivering higher productivity and satisfaction. From managing data to providing personalized support, their role is transformative.
As bridges between human needs and automation, AI agents are reshaping intelligent assistance. Their learning ability, adaptability, and round-the-clock functionality make them indispensable in modern business and technology strategies.
Key Takeaways
- AI agents use machine learning to make intelligent, human-like decisions.
- AI agents analyze real-time IoT data for faster, smarter decisions.
- Companies prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems.
- AI agents streamline operations and automate workflows across industries.
- AI agents are driving innovation in healthcare, logistics, and smart homes.
- AI agents learn from experience, enabling continuous optimization and smarter decisions.
- Developers and policymakers ensure ethical, human-centric AI development.
- Companies adopting AI agents achieve agility, growth, and industry relevance.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perform tasks and make decisions on behalf of humans. They interact with their environment, adapt to new situations, and operate with a goal-oriented approach. These systems use artificial intelligence to analyze data, identify patterns, and take actions that achieve specific objectives.
Core Functions of AI Agents
Autonomous Decision-Making
AI agents operate independently, making decisions based on pre-defined goals and learned experiences. Unlike static systems, they don’t rely on manual input for every action. Instead, they analyze incoming data, recognize patterns, and determine the most effective approach. This allows them to make quick, accurate decisions even in complex environments.
Autonomous decision-making is essential in applications like chatbots, recommendation engines, and self-driving cars, where timely actions are critical. By learning from past decisions, they improve future choices, offering smarter, more personalized responses over time.
Goal-Oriented Operation
AI agents function with a clear, goal-driven approach. Every action they take is aligned with specific objectives, which are often set by users or programmed rules. This goal-oriented behavior enables them to prioritize tasks, ensuring that high-priority actions are completed first.
For example, an AI chatbot prioritizes responding to urgent queries over less critical requests in customer service.
Their ability to focus on clearly defined goals helps reduce inefficiencies and improves task completion rates. By optimizing for specific outcomes, AI agents ensure that business objectives are met more effectively.
Interactive Learning and Adaptation
One of the most significant functions of AI agents is their ability to learn and adapt. Through machine learning and feedback loops, they continuously refine their performance. After each task or action, AI agents analyze the results to understand what worked well and what didn’t. This allows them to improve future responses without manual reprogramming.
For instance, AI recommendation engines like those on e-commerce platforms learn from user preferences to suggest better products over time. This dynamic learning ability is key to creating more personalized and context-aware interactions for users.
Environmental Interaction
AI agents gather information from their surroundings to inform decision-making. They collect real-time data from sensors, user inputs, or online sources and process it to guide their next actions. This interaction with the environment enables them to provide context-specific solutions.
For instance, virtual assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant respond to voice commands by understanding user intent and the context of the request. In robotics, AI agents interact with physical objects to navigate spaces or perform tasks like picking and placing items. This capability allows them to operate in real-world environments with precision.
System Integration
AI agents do not work in isolation; they are designed to connect and integrate with other systems and platforms. Through APIs and software integrations, they interact with external applications to enhance their capabilities. For example, in customer support, AI chatbots integrate with CRM tools to provide agents with customer history and data. In business automation, AI agents connect with enterprise software like ERPs and HR systems to automate workflows and process large datasets.
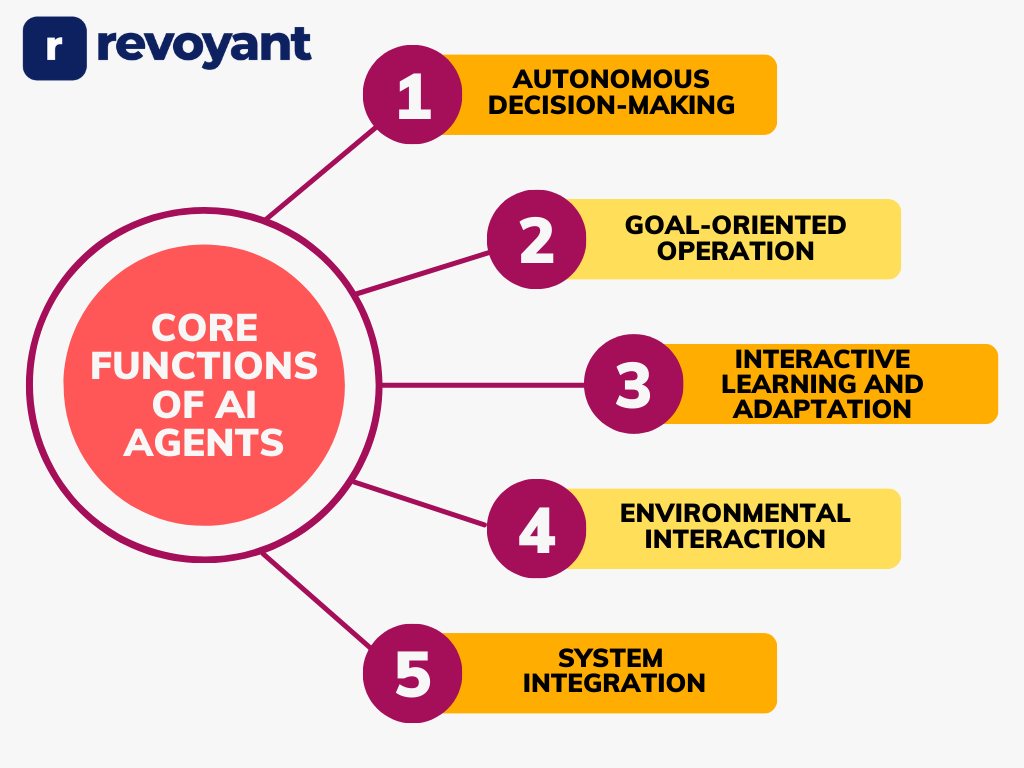
This seamless integration allows AI agents to operate as part of a larger ecosystem, enabling faster data exchange, process automation, and cross-platform functionality.
Examples in Various Industries
AI agents are intelligent systems used across various industries such as customer service (e.g., chatbots), logistics (e.g., route optimization), healthcare (e.g., diagnostic tools), finance (e.g., algorithmic trading), IT operations (e.g., system monitoring), retail (e.g., personalized shopping), manufacturing (e.g., robotics), education (e.g., intelligent tutoring). Real-world examples include Siri (Apple), Alexa (Amazon), Netflix recommendations.
- Chatbots (e.g., Siri) manage customer inquiries more efficiently than humans.
- Diagnostic tools use algorithms (e.g., IBM Watson) to analyze symptoms more accurately than doctors.
- Algorithmic trading enables computers to trade stocks faster than humans can react.
- System monitoring tools prevent downtime, proactively maintaining business continuity twenty-four-seven non-stop every day.
- Personalized shopping enhances customer satisfaction, encouraging an uplift in organic sales.
- Robots optimize production workflows safely, operating alongside human colleagues 24/7, non-stop.
- Intelligent tutoring provides adaptive learning pathways remotely, catering to diverse student requirements and scaling learning outcomes to universally accessible education consistently!
Key Concepts Behind AI Agent Technology
AI agent technology depends on environmental interaction. Agents gather information from their surroundings through sensors or data feeds, allowing appropriate responses. Purpose-driven behavior influences decision-making processes within these systems, enabling adaptability based on experience acquired through repeated interactions.
This process leads to refined outcomes through ongoing improvement cycles facilitated by data exchange between collaborating units using established communication paths within respective agent networks.
Environment Interaction
Artificial intelligence (AI) engages dynamically with external systems, consistently performing actions within its surroundings while receiving continuous feedback. AI systems gather real-world data from external sources, such as sensors or databases. By processing this information through machine learning algorithms, these systems achieve continuous improvement through adaptive responses developed through feedback loops during each iteration.
This approach aims to optimize overall performance across networks while minimizing inefficiencies at every stage of implementation. Over time, these processes work toward achieving full autonomy without compromising quality or fundamental principles.
Remaining curious and open to new insights encourages continuous learning and personal growth. Patience and perseverance can help navigate life’s challenges, leading to transformational change and eventual success. Each individual chooses their path and destination, with the journey offering opportunities for growth and fulfillment along the way.
Goal-Oriented Behavior
Task implementation utilizes gathered information, such as airline schedules, enabling users, such as travel planners, to focus on determining travel arrangements based on optimal dates. This approach helps users make informed decisions regarding affordable flights that align with their objectives, initiating the necessary steps toward completion.
It ensures users reach their destinations efficiently under time constraints, achieving desired outcomes while meeting specific requirements and maximizing effectiveness. This process results in successful progress, allowing users to achieve their goals promptly while maintaining momentum, monitoring progress, and advancing goals without interruption.
It promotes comprehensive solutions, efficiently achieving milestones and leading to successful completion while maintaining awareness of broader objectives. This systematic approach eliminates errors, encouraging meaningful progress and overall satisfaction by analyzing efforts and achieving closure that empowers further success.
Learning and Adaptation
Learning agents use machine learning to enhance their performance over time. They improve their ability to handle tasks such as financial trading strategies. Model-based agents adjust to changes by utilizing internal system models.
This approach allows them to regulate inventory levels effectively. Key principles behind AI agent technology include learning and adaptation. AI agents can acquire knowledge from data and adjust to evolving situations. They employ reinforcement learning, adaptive behavior, and self-learning systems. Machine learning algorithms enable AI agents to boost their performance. They gain insights from data and make more informed decisions.
For instance, machine learning can optimize financial trading strategies. AI agents can adapt to shifting circumstances and make improved decisions, allowing them to carry out tasks more effectively.
Decision-Making Logic of AI Agents
AI agents rely on decision-making logic to select actions based on their goals, objectives, and real-time inputs. This logic is programmed using algorithms like logical reasoning and cognitive processes. By analyzing data from sensors, user inputs, and software applications, AI agents make context-aware decisions tailored to specific situations.
Core concepts include environment interaction, where agents process data to understand their surroundings, and goal-oriented behavior, which ensures that actions are aligned with specific objectives. They also incorporate machine learning, enabling them to adapt and improve over time. Communication and collaboration with other systems or humans allow AI agents to operate effectively in dynamic, real-world environments.
These capabilities make AI agents essential for applications like automation, customer support, and robotics, where adaptability and decision-making are crucial.
Communication and Collaboration
Expanding on decision-making logic, AI agents advance by engaging with their surroundings and other agents. This engagement plays a crucial role in communication and cooperation. AI agents employ multiple techniques to exchange information with humans, other agents, and systems. They distribute data, synchronize actions, and operate collectively to accomplish shared objectives.
In customer service, for example, AI-driven chatbots work alongside human agents to address intricate challenges. Humans offer support and supervision to achieve precision in outcomes, reviewing AI outputs and addressing mistakes as required.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents are classified into four main categories based on their operational style, adaptability, and decision-making capabilities. Each type of agent serves specific use cases and is suitable for different industries and applications.
Reactive Agents
Reactive agents operate on a simple “sense and respond” model, reacting instantly to environmental changes without planning for future actions. They follow predefined rules to make decisions, which allows for fast, real-time responses. Reflex agents are a classic example, as they rely on fixed logic to react to inputs.
These agents are commonly used in simple systems like thermostats, autonomous robots, and video game characters that respond to player movements. Their primary strength is speed, but they have no capacity for long-term planning.
Deliberative Agents
Deliberative agents plan their actions based on reasoning and future predictions. Unlike reactive agents, they consider possible future states and the impact of their actions before making a decision. These agents use logical reasoning and planning methods to achieve specific objectives.
For instance, a deliberative agent controlling delivery truck routes can assess traffic patterns, road closures, and delivery schedules to select the most efficient route. As conditions change, like weather or traffic, the agent can update its plan to maintain optimal performance. Deliberative agents are ideal for applications that require foresight, such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and scheduling software.
Hybrid Agents
Hybrid agents combine the fast, real-time responses of reactive agents with the forward-thinking planning of deliberative agents. This hybrid model allows them to handle complex tasks in dynamic environments. Hybrid agents balance immediate responsiveness with long-term planning, offering a flexible approach to problem-solving. They typically operate in multi-agent systems, where multiple agents collaborate to achieve shared goals.
For example, self-driving cars use hybrid agents to make real-time driving decisions (like braking for obstacles) while also following a planned route. This blend of adaptability and foresight makes hybrid agents essential for robotics, autonomous navigation, and AI assistants.
Learning Agents
Through machine learning, learning agents continuously evolve and improve their decision-making abilities. They refine their actions and strategies based on new experiences, making them smarter over time. These agents analyze data, recognize patterns, and adjust their behavior accordingly.
For instance, learning agents in financial trading use past market data to identify profitable opportunities and fine-tune their investment strategies. Self-learning algorithms enable these agents to adjust to changing market conditions, which makes them highly valuable in areas like predictive analytics, recommendation engines, and customer service bots.
As they learn from their experiences, their decision-making processes become more efficient and accurate.
Which AI Agent is Right for Your Needs?
Each type of AI agent has distinct strengths and is suited for specific industries and applications:
- Reactive agents are ideal for simple, real-time decision-making.
- Deliberative agents are best for tasks requiring planning and foresight.
- Hybrid agents excel in dynamic, fast-changing environments.
- Learning agents are perfect for use cases that require continuous adaptation and improvement, like trading bots and recommendation systems.
These agents play a pivotal role in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and autonomous systems. By selecting the right type of AI agent, businesses can automate operations, increase efficiency, and drive growth in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
Top AI Agent Software – Features, Pricing, and Use Cases
Top AI agent software for 2025 includes:
| Software | Features | Pricing | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appian | Business process orchestration, AI-related insights, tools, and automation solutions | Custom pricing for enterprises | Business workflow automation, customer service, logistics, and supply chain management |
| Pegasystems | Business process management, customer relationship management, and AI-powered automation | Custom pricing for enterprises | Customer service, marketing, and sales automation |
| Other software | Varying features, including machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision | Varying pricing models, including subscription-based and custom pricing | Varying use cases, including healthcare, finance, and retail |
Appian’s AI agent software has been recognized as a leader in the 2023 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms and has reported a 95% increase in process speed, according to the Forrester Total Economic Impact of Appian 2023.
AI Agents in Action
AI agents are transforming industries by automating processes, enhancing decision-making, and enabling smarter operations. From customer service to manufacturing, they are driving efficiency, accuracy, and personalization. Here’s a closer look at how AI agents are being utilized across key sectors.
Customer Service – Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots streamline customer interactions by handling routine tasks like responding to inquiries, managing emails, and resolving customer queries. These agents operate across messaging apps, websites, and phone calls, providing 24/7 support. Businesses benefit from faster response times, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced operational load. Platforms like Zendesk leverage AI chatbots to deliver exceptional support experiences.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
AI agents play a pivotal role in logistics, enabling real-time tracking, demand forecasting, and optimized inventory management. Analyzing demand fluctuations helps companies maintain proper stock levels and minimize waste. Utility-based agents assist with project scheduling, ensuring on-time delivery and efficient load balancing. Tools like FourKites are leading logistics platforms that use AI agents to streamline supply chain operations.
Healthcare – Diagnostics and Patient Management
AI agents support healthcare providers by enhancing diagnostics and patient care. They analyze medical images like X-rays and MRIs to detect diseases, improving the speed and accuracy of diagnoses. Additionally, AI-driven systems manage patient records, automate administrative tasks, and offer data-driven treatment recommendations. Tools like IBM Watson Health use AI to support clinical decisions, reduce errors, and enable personalized care.
Finance – Fraud Detection and Automated Advice
In the finance sector, AI agents detect fraudulent transactions and support algorithmic trading. Reflex agents identify unusual activity in real-time, helping financial institutions protect customers and prevent financial losses.
Automated advisory agents offer personalized financial advice by analyzing user data and market trends. Companies like Plaid and Zest AI leverage AI agents to provide smarter financial services and reduce risks.
IT Operations – System Monitoring and Automation
IT departments use AI agents to monitor systems for anomalies, automate incident responses, and maintain system uptime. These agents detect system failures, automate fixes, and notify IT teams before disruptions occur. Automated monitoring tools like Dynatrace and New Relic allow enterprises to avoid downtime, improve system reliability, and boost operational efficiency.
Retail – Personalized Shopping Experiences
Retailers use AI agents to offer personalized shopping experiences. By analyzing customer preferences, shopping history, and behavior, AI agents recommend products, suggest deals, and create tailored shopping journeys. Retailers can also use AI agents to offer personalized promotions, making the shopping experience more relevant. Platforms like Amazon Personalize and Bloomreach empower e-commerce stores with AI-driven product recommendations and personalized marketing.
Manufacturing – Robotics and Quality Control
In manufacturing, AI agents power robotic systems that perform assembly, inspection, and precision engineering. Robotic agents ensure production accuracy, reduce defect rates, and detect product faults early. With automated inspection systems, manufacturers can monitor quality control in real-time. Industrial robotics platforms like Fanuc and ABB Robotics use AI agents to automate repetitive, high-risk, and labor-intensive tasks, boosting production efficiency.
Education – Intelligent Tutoring Systems
AI agents support education by personalizing learning experiences. Intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) analyze students’ strengths and weaknesses, offering customized lessons and interactive feedback. These agents provide one-on-one guidance, empowering students to learn at their own pace. AI e-learning agents personalize learning journeys, making education accessible and adaptive for every student.
AI agents are revolutionizing industries by enabling smarter, faster, and more personalized experiences. As technology evolves, their role in automating workflows, managing data, and supporting real-time decision-making will continue to expand, driving innovation across sectors.
Benefits of AI Agents for Organizations
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
AI agents play a pivotal role in enhancing organizational efficiency and productivity. Automating routine tasks allows employees to focus on more strategic and creative work. Reports indicate that AI-driven automation can accelerate processes by up to 95%. Companies like Appian have seen significant gains in process speed through AI solutions. Workflow optimization, task management, and reduced processing times lead to higher productivity levels across various departments. As a result, teams can achieve more in less time, driving business growth.
Cost Savings Through Automation
Organizations experience substantial cost savings when they integrate AI agents into their operations. Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, saving time and minimizing the likelihood of errors. Tasks like customer support, data entry, and assembly line production become more efficient, as seen with the use of chatbots and industrial robots. Companies can reinvest these savings into strategic initiatives, such as product development or market expansion. By enabling round-the-clock operations, AI agents boost overall productivity, ensuring that companies maximize their resources.
Enhanced Customer Experience
AI agents play a vital role in improving customer interactions. Virtual assistants and chatbots provide instant responses to customer inquiries, enhancing communication efficiency by over 90%. By using AI to offer personalized product recommendations and support, companies like Amazon and Zendesk deliver tailored experiences that drive customer satisfaction. AI-powered assistants can schedule appointments, process orders, and provide real-time assistance. Businesses that adopt AI-driven customer service solutions report higher customer retention and improved brand loyalty.
Data-Driven Decision Making
AI agents enable smarter decision-making by processing large datasets to deliver actionable insights. Machine learning algorithms analyze data and identify patterns that support predictive analytics. Companies can make more informed business decisions with tools like Tableau and IBM Watson. From forecasting customer demand to optimizing inventory, AI agents use data-driven insights to guide organizational strategy. This approach helps businesses minimize risk, improve efficiency, and seize growth opportunities.
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the standout benefits of AI agents is their ability to scale operations. Unlike manual systems that require more staff as demand grows, AI agents can handle increasing workloads without proportional cost increases. AI systems, such as UiPath, adapt to changing business demands by processing larger datasets and managing additional tasks without interruption. This scalability ensures that businesses remain agile, responsive, and prepared to handle growth. As a result, companies can expand without hiring additional human resources, boosting cost-efficiency and operational capacity.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations that leverage AI agents gain a significant competitive edge. AI technology enhances efficiency, automates processes, and provides better customer service. Companies use AI agents to innovate and stay ahead of competitors. Automation-driven improvements in speed, accuracy, and personalization give businesses a clear advantage. By adopting AI agents, companies position themselves as industry leaders and strengthen their market presence. This strategic advantage supports long-term growth, adaptability, and resilience.
Improved Employee Satisfaction
AI agents reduce employee workloads by handling repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more engaging, high-value activities. This shift increases job satisfaction, as employees can prioritize creative and strategic responsibilities. Automation tools streamline workflows, reducing the burden of administrative tasks. Employees feel more engaged, experience less burnout, and report higher job satisfaction, which in turn improves overall company culture and employee retention rates.
Challenges and Risks of AI Agents
AI agents bring significant benefits to organizations, but they also introduce certain challenges. These challenges require oversight, security measures, and regulatory compliance to ensure safe and effective use. Below are some key challenges and methods to address them.
Autonomy and Control Issues
AI agents operate autonomously, meaning they make independent decisions based on data inputs and learned patterns. While this autonomy boosts efficiency, it also introduces potential challenges. One key issue is data poisoning, where incorrect or manipulated data can influence AI decision-making.
For instance, altered pricing data could disrupt cost predictions and resource allocation in supply chain management.
Another challenge is ensuring that AI agents make sound decisions. As AI agents continue to learn and adapt, there is a chance for incorrect adjustments. This is why oversight is essential. Organizations must set clear boundaries and controls to ensure AI agents operate within acceptable guidelines. By implementing continuous monitoring and quality checks, companies can maintain consistent, reliable decision-making from their AI systems.
Security and Compliance Concerns
AI systems analyze large datasets, which may include sensitive user data. This makes security and compliance critical. Organizations must ensure that AI-driven systems adhere to data privacy regulations such as HIPAA for healthcare or GDPR for global data privacy. Protecting sensitive customer information is essential for maintaining trust and avoiding compliance issues.
Data security measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls help safeguard sensitive information. Companies should also ensure that the AI algorithms themselves are secure, as hackers may try to exploit vulnerabilities.
Regular risk assessments, threat detection, and system audits can help identify and fix potential security gaps. With proper security protocols in place, companies can protect user data and maintain compliance with legal and regulatory standards.
Mitigating Challenges and Risks
Mitigating challenges posed by AI agents requires a proactive strategy to ensure secure and effective operations. Companies can implement zero-trust policies to verify every user and device before granting access, reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure. Data access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can view sensitive information, while human oversight allows experts to review and validate AI-generated outputs, ensuring quality and accuracy.
Data governance establishes guidelines for data collection, storage, and usage, promoting data security and integrity. Together, these measures create a secure, efficient, and well-managed AI environment that minimizes risks and maximizes operational efficiency.
Emerging Trends in AI Agents
Advances in Machine Learning and AI Capabilities
AI agents are becoming more sophisticated as advanced machine learning algorithms and cognitive computing are integrated. These advancements enable AI agents to learn from data, recognize patterns, and make human-like decisions.
Technologies such as deep learning and neural networks allow AI agents to process large volumes of information quickly, enhancing decision-making speed and accuracy.
Research in cognitive and emotional intelligence aims to improve AI agents’ ability to understand and respond to human emotions, facilitating more natural and human-like interactions. These improvements open up new possibilities for industries like healthcare, finance, and customer service, where empathetic interactions and smarter decision-making are crucial.
Integration with IoT and Big Data
AI agents are increasingly being integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, creating a connected ecosystem where agents can collect and analyze real-time data from physical devices. This integration allows AI agents to make faster, data-driven decisions.
For example, in smart homes, AI agents connected to IoT devices like thermostats or security cameras can manage energy use and enhance home security.
Similarly, in supply chain management, AI agents leverage IoT sensors to monitor inventory, track shipments, and predict delivery times.
Additionally, big data enables AI agents to process vast datasets and identify trends, offering deeper insights and improving forecasting. This data-driven approach helps businesses optimize workflows, reduce costs, and boost efficiency.
Ethical and Governance Considerations
As AI agents become more autonomous and integrate with IoT and big data systems, ethical and governance considerations are becoming essential. Companies must ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI-driven decision-making. Ethical guidelines aim to prevent bias in AI models, particularly in areas like loan approvals, hiring, and healthcare.
Organizations are implementing responsible AI frameworks to ensure that AI agents operate within ethical boundaries and adhere to regulations like GDPR for data privacy. To foster public trust, developers, policymakers, and industry leaders are working together to create governance frameworks that ensure AI technology is used responsibly.
Establishing transparent systems, conducting regular audits, and fostering human oversight help organizations ensure ethical AI adoption.
Conclusion
AI agents are transforming technology with smarter, connected, and ethically guided systems. Leveraging advancements in machine learning and IoT, they enable real-time data analysis, enhancing industries like healthcare, logistics, and smart home automation.
To foster trust and innovation, companies prioritize transparency, fairness, and data privacy, ensuring responsible AI governance. This balance of autonomy and accountability drives growth while addressing ethical concerns.
The future of AI agents promises personalized customer experiences, efficient operations, and increased productivity. By embracing these trends and fostering human-centric development, businesses can gain a competitive edge and create sustainable, innovative solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions about AI Agents
What are AI agents, and how do they function in everyday applications?
AI agents are software entities that perform specific tasks autonomously by processing data, analyzing patterns, and making decisions. They leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning models to understand inputs and deliver accurate outputs, making them highly useful in various industries.
How do AI agents use machine learning and real-time data?
AI agents rely on machine learning to improve their performance over time. By processing real-time data, they identify trends, predict outcomes, and adapt to new scenarios, ensuring their responses are both timely and relevant.
What role does natural language processing (NLP) play in AI agents?
Natural Language Processing enables AI agents to understand and respond to human language. It allows these systems to interpret text or speech, providing user-friendly interactions in applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer support tools.
How do AI agents integrate with existing business systems?
AI agents are designed to seamlessly connect with existing business tools, such as CRM, ERP, or analytics platforms. This integration ensures smooth data flow and enhances decision-making processes across departments.
What industries benefit most from AI agent technology?
AI agents are widely used in industries like healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and customer service. They enhance efficiency, provide personalized experiences, and support tasks such as scheduling, data analysis, and customer interaction management.



