The B2B buying process is a structured journey that involves multiple stakeholders, careful evaluations, and a focus on long-term value. Unlike individual purchases, business decisions require collaboration across teams, aligning priorities such as budget, functionality, and return on investment.
Organizations begin by identifying a challenge or opportunity that needs a solution. From there, they explore potential options, compare vendors, and evaluate solutions based on specific needs. Each stage involves thorough research, discussions, and approvals to ensure the right fit. Factors like integration with existing systems, scalability, pricing models, and post-purchase support play a key role in the final decision.
As B2B buying behaviors evolve, companies are leveraging digital tools, data-driven insights, and automation to streamline decision-making. Understanding this process helps vendors, marketers, and sales teams provide relevant information at the right time, building trust and driving successful outcomes. A well-structured approach to B2B purchasing ensures businesses invest in solutions that align with both immediate and long-term goals.
Key Takeaways
- The B2B buying process involves multiple stages, including identifying needs, researching solutions, evaluating vendors, making a decision, and post-purchase assessment.
- Decision-making in B2B transactions is influenced by factors such as ROI, product functionality, integration, vendor reputation, and customer support.
- Businesses can speed up the buying process by offering self-service options, leveraging B2B marketplaces, and providing personalized marketing content.
- Strong post-purchase engagement, including customer support and seamless onboarding, encourages long-term relationships and repeat business.
- Companies that simplify procurement workflows and provide clear, relevant information at each stage create a more efficient and buyer-friendly experience.
What is a B2B Buying Process?
The B2B buying process is a structured approach that businesses use to identify, evaluate, and purchase products or services that support their operations and long-term goals. Unlike consumer purchases, which are often based on personal preferences and quick decisions, B2B transactions involve multiple stakeholders, thorough research, and a focus on return on investment.
This process typically begins with recognizing a need, whether it’s improving efficiency, expanding capabilities, or meeting regulatory requirements. Once the need is established, businesses conduct research to explore potential solutions, compare vendors, and assess which options align best with their objectives. This phase includes gathering insights from industry reports, customer reviews, and direct vendor interactions.
After shortlisting options, decision-makers evaluate pricing, features, integration capabilities, and long-term scalability. The procurement stage involves negotiating contracts, securing internal approvals, and finalizing agreements. Once a solution is implemented, businesses continue to assess its performance, ensuring it delivers value.
Key Stages of the B2B Buying Process
The B2B buying process follows a structured path where businesses carefully evaluate their needs, explore solutions, and make decisions that align with long-term goals. Unlike individual purchases, this process involves multiple stakeholders, extended research, and thorough assessments before finalizing a decision. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring that the chosen solution delivers value and supports business growth.
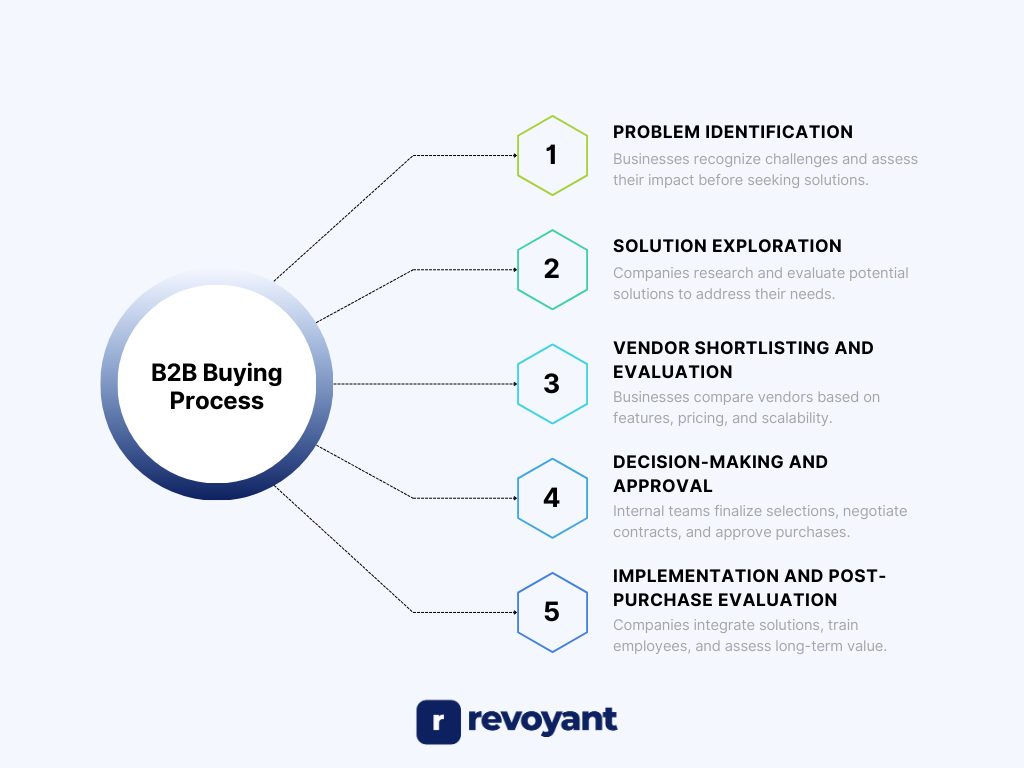
Problem Identification
The process begins when a company recognizes a challenge or an opportunity that requires action. This could be the result of operational inefficiencies, evolving market demand, compliance requirements, or a need to stay competitive. Internal teams discuss the issue to determine its impact on business processes, revenue, or customer experience.
Once the problem is clearly defined, they decide whether an external solution is necessary. Without a well-articulated problem, businesses struggle to find the right solution, making this the foundation of the entire B2B buying journey.
Solution Exploration
After identifying the need, businesses start researching potential solutions. This stage involves gathering information from industry reports, peer recommendations, vendor websites, and independent reviews. Companies explore different categories of solutions to understand which approach best addresses their requirements.
Discussions take place within teams to assess what type of product or service would fit best, whether it’s a new software system, an outsourced service, or an upgraded version of an existing tool. Businesses at this stage focus on understanding their options before narrowing them down to a few serious contenders.
Vendor Shortlisting and Evaluation
With well-defined requirements, businesses begin evaluating potential vendors. This phase involves comparing different providers based on product functionality, ease of implementation, customer support, and pricing models. Businesses often schedule product demos, attend vendor presentations, and review case studies to assess how each solution performs in real-world scenarios.
They may also issue a Request for Proposal (RFP) or Request for Quotation (RFQ) to collect detailed bids from vendors. Decision-makers carefully assess how each option aligns with their strategic objectives before moving forward with a shortlist of finalists.
Decision-Making and Approval
The final selection requires internal approvals, contract negotiations, and legal review. Executive teams, finance departments, and procurement specialists assess whether the investment aligns with budget constraints and business goals. Legal teams may examine contracts to ensure compliance with company policies, while IT teams confirm the solution’s compatibility with existing systems.
This stage can involve multiple rounds of discussions as businesses negotiate pricing, service-level agreements (SLAs), and implementation timelines. Once all requirements are met, the company gives the final approval, and contracts are signed.
Implementation and Post-Purchase Evaluation
Once the purchase is finalized, businesses move into the implementation phase, where vendors work closely with internal teams to set up the solution, migrate data if necessary, and provide employee training. A well-structured onboarding process plays a crucial role in ensuring high adoption rates and seamless integration with existing workflows. Performance benchmarks are often established to measure effectiveness, helping businesses track whether the solution aligns with their expectations and operational goals.
After implementation, businesses continuously evaluate the solution’s performance to determine if it meets efficiency, cost, and user satisfaction expectations. Ongoing support, system updates, and scalability are critical considerations when assessing long-term viability. Companies that see measurable value often choose to renew contracts or expand usage, while those facing limitations may explore alternatives or renegotiate terms.
Who Contributes to the B2B Buying Process?
The average B2B buying decision involves six to ten people, each equipped with over four pieces of information they have independently gathered during their decision-making process.
The typical B2B buying process includes the following five roles:
- Initiator: The person who identifies a problem and starts the search for a solution. This role triggers the buying process.
- Influencers: Individuals who shape the opinions and preferences of the decision-makers. Influencers can be internal, like department heads, or external, such as industry experts on platforms like LinkedIn.
- Decision Maker: The person who authorizes the purchase. This role often includes senior figures like store owners, CEOs, heads of accounting, or business development managers.
- Buyer: Responsible for placing the order, negotiating prices, and ensuring purchase terms are met. In large retail settings, this role is typically filled by a buying or merchandising manager.
- End User: The individual who will use the product or service on a daily basis. For instance, if a company is purchasing new office chairs, the office workers who will use them are the end users. Sometimes, the end user may also be the initiator if they raise an issue that leads to the purchase.
Key Factors Influencing the B2B Buying Process
Businesses make purchasing decisions based on a combination of internal needs, market conditions, and strategic objectives. Unlike individual consumer purchases, which can be influenced by personal preferences or emotions, B2B buying process decisions are driven by practical considerations, measurable impact, and long-term value. Several key factors play a role in shaping how companies approach procurement and vendor selection.
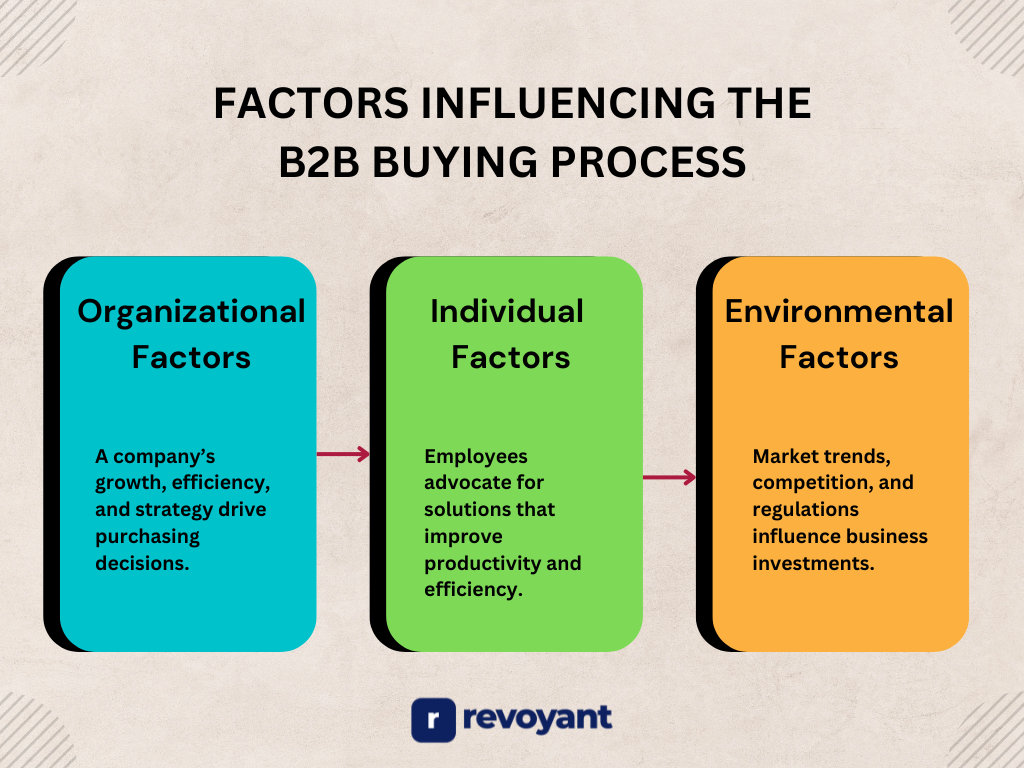
Organizational Factors
A company’s overall goals, growth strategies, and operational challenges significantly influence its purchasing decisions. Businesses invest in new products and services to enhance efficiency, scale operations, or address evolving market demand generation. If a company is expanding to new locations, it may require cloud-based collaboration tools, supply chain management systems, or automated customer support solutions to streamline processes.
Similarly, if revenue growth is a priority, leadership may explore CRM software, marketing automation, or data analytics tools that provide deeper insights into customer behavior. Organizational restructuring, mergers, or leadership changes can also trigger the need for new solutions that align with updated business strategies.
Individual Factors
While B2B purchases are made at an organizational level, they are often initiated by individuals within the company who experience specific challenges in their day-to-day roles. Employees who face inefficiencies, repetitive tasks, or outdated systems are likely to advocate for better solutions. For example, if a finance team struggles with manual invoicing, they may push for an automated accounting system to improve accuracy and save time.
Similarly, if customer support agents find it difficult to manage high call volumes, they may request AI-driven chatbots or ticketing systems to enhance response times. Employee feedback plays a crucial role in influencing procurement decisions, especially when the proposed solution directly impacts productivity, satisfaction, and overall workplace efficiency.
Environmental Factors
Market trends, industry competition, and external economic conditions also shape B2B buying behavior. Companies closely monitor shifts in technology, regulatory changes, and competitive advancements to ensure they remain relevant and efficient. For example, the rapid rise of e-commerce has prompted traditional retailers to invest in digital transformation initiatives, such as omnichannel sales platforms and AI-driven customer insights.
Businesses in highly regulated industries, such as healthcare or finance, may adopt compliance-focused software solutions to stay ahead of evolving legal requirements. The pressure to innovate and meet customer expectations pushes organizations to invest in tools that enhance agility and operational resilience.
How to Streamline and Speed Up the B2B Buying Process
The B2B buying process often takes time due to multiple decision-makers, extensive evaluations, and budget approvals. Unlike consumer purchases, which can be made quickly by individuals, B2B transactions require input from various teams and careful planning. While these steps are necessary, businesses can take proactive measures to simplify decision-making, reduce delays, and create a more efficient B2B buying experience.
Make Self-Service a Priority with E-commerce
Many business buyers prefer to research and make decisions independently before engaging with a sales team. A well-structured e-commerce platform gives them the flexibility to explore options, compare pricing, and place orders at their own pace. Platforms like Shopify make it easier to manage both B2B and B2C storefronts, allowing buyers to access wholesale pricing, set payment terms, and generate invoices without waiting for manual approvals.
A seamless online purchasing process not only reduces the time spent on back-and-forth communication but also improves overall customer satisfaction.
Use B2B Marketplaces to Simplify Procurement
B2B marketplaces such as Amazon Business and Alibaba have made it easier for companies to source products, compare vendors, and make informed purchasing decisions. These platforms provide a centralized location where buyers can evaluate pricing, check availability, and read reviews, all of which contribute to faster decision-making.
Businesses benefit from pre-established supply chain networks and trusted vendor ratings, reducing uncertainty and streamlining procurement. By making their products available on these platforms, suppliers increase visibility and provide buyers with a more efficient purchasing experience.
Deliver Targeted Information with Personalized Marketing
B2B buyers expect a level of personalization similar to what they experience in direct-to-consumer purchases. Providing relevant and timely information at different stages of the B2B buying process helps decision-makers move forward with confidence. Case studies, industry reports, white papers, and expert-led webinars address specific pain points and demonstrate the value of a solution in a way that resonates with the buyer.
Research from Gartner suggests that companies that receive personalized content tailored to their needs make decisions more quickly and with greater certainty. Rather than presenting generic sales pitches, businesses that provide insights aligned with the buyer’s industry, company size, and challenges make the purchasing process smoother and more efficient.
Strengthen Relationships with Post-Purchase Engagement
A strong post-purchase strategy keeps buyers engaged and encourages repeat business. The relationship between a vendor and a business doesn’t end when a purchase is made—it extends into implementation, ongoing support, and renewal discussions. Businesses that provide responsive customer service, proactive product updates, and an easy reordering experience help buyers maximize the value of their investment.
Features such as order history, subscription-based purchasing, and dedicated account management reduce friction and make future transactions more seamless. A positive post-purchase experience builds long-term trust, leading to higher customer retention and stronger business relationships.
Conclusion
Streamlining the B2B buying process requires a combination of technology, strategic communication, and a buyer-centric approach. Businesses that simplify research, provide self-service options, and deliver personalized insights can significantly reduce delays in decision-making. Offering an intuitive e-commerce experience and leveraging established marketplaces allows buyers to access information and complete transactions with fewer obstacles. When purchasing is straightforward and transparent, businesses are more likely to commit with confidence.
Beyond the initial sale, long-term success depends on maintaining strong relationships. A seamless onboarding process, proactive customer support, and an easy renewal experience contribute to continued trust and loyalty. Buyers appreciate efficiency, and companies that minimize complexity while delivering real value set themselves apart from competitors.
As buyer expectations continue to shift, companies that embrace a more fluid, self-directed purchasing experience will see faster sales cycles and stronger retention rates. By focusing on what makes the process easier—from research to purchase to post-sale engagement—businesses can build lasting partnerships, improve customer satisfaction, and drive consistent growth in an increasingly competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main stages of the B2B buying process?
The B2B buying process involves several stages, including identifying a need, researching potential solutions, defining requirements, shortlisting vendors, evaluating options, making a final decision, and assessing post-purchase performance. Each step ensures that the chosen product or service aligns with business objectives.
How do businesses research vendors before making a purchase?
Companies explore vendor options by reviewing industry reports, reading customer testimonials, comparing features on B2B marketplaces, attending webinars, and requesting product demos. Many businesses also seek peer recommendations or issue RFPs to gather detailed proposals from potential vendors.
What factors influence B2B purchasing decisions?
Decisions are driven by factors such as return on investment, product functionality, integration capabilities, vendor reputation, customer support, and long-term scalability. Businesses prioritize solutions that improve efficiency, reduce costs, and align with their operational needs.
How can businesses speed up the buying process?
To reduce delays, companies can implement self-service e-commerce options, use B2B marketplaces for faster procurement, personalize marketing efforts with relevant content, and streamline internal approval workflows. Clear communication among decision-makers also helps accelerate purchasing timelines.
Why is post-purchase engagement important?
Post-purchase engagement strengthens vendor-buyer relationships, ensuring smooth implementation and long-term satisfaction. Businesses benefit from proactive customer support, training resources, and an easy reordering experience, which contributes to higher retention rates and ongoing value.

