Artificial intelligence (AI) has redefined the way businesses operate, and AI agent software stands as a pivotal innovation driving this transformation. From automating tasks to offering seamless interactions, these intelligent systems are shaping how organizations interact with their customers and optimize internal processes.
AI agent software combines the power of machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to deliver solutions that adapt to user needs in real-time. Whether it’s improving customer service, streamlining operations, or providing advanced data insights, these tools are proving indispensable for businesses looking to remain competitive.
This guide will explore the key features, benefits, and practical applications of AI agent software, helping you understand how it fits into various industries and can revolutionize day-to-day operations.
Key Takeaways
- AI agent software uses natural language processing and machine learning to work on its own and make decisions.
- It improves efficiency, customer experiences, cost savings, and scalability, with predictions of increasing human productivity by 40%.
- AI agent systems combine probabilistic and deterministic elements, and modularization helps distinguish deterministic, predictive, and creative components.
- Examples of AI agents include chatbots, virtual assistants, and autonomous vehicles, which are used in industries such as customer service, healthcare, and finance to automate tasks and improve decision-making.
Key Topics Covered in the Guide
AI agent software has become increasingly important today due its ability automate tasks autonomously using large language models (LLMs) like IBM Watson Assistant.
- Modular design promotes composability enabling organizations create different systems easily through Compound AI Systems (CAIS) like Mosaic framework by Databricks providing end-to-end system building capabilities allowing easier management extensibility deterministic access consistent responses modular support autonomous task automation notable platforms like Odin, UiPath, and Kore.ai.
- Key features including Natural Language Processing machine learning capabilities integration existing systems task automation customization scalability security privacy
- Benefits including efficiency productivity customer experiences cost savings decision-making scalability growing businesses better insights improved personalization forecasting scheduling
- Real-world applications customer support HR healthcare marketing sales e-commerce inventory management supply chain logistics scheduling patient communication record management recruitment employee engagement lead generation campaign automation
What is AI Agent Software?
AI agent software refers to intelligent programs that use artificial intelligence to perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. These systems are designed to mimic human behavior, enabling them to learn, reason, and make decisions based on data.
Key features of AI agents include natural language understanding, data analysis, task automation, and decision-making capabilities. They are often deployed in environments like customer service, e-commerce, healthcare, and finance, where they can streamline operations and enhance user experiences.
By automating repetitive tasks and analyzing complex datasets, AI agents reduce manual workload and provide actionable insights. These tools can operate independently, following human-defined goals, making them an essential component of modern business strategies. From chatbots to advanced predictive analytics systems, AI agents are reshaping how technology interacts with users and drives efficiency.
How AI Agent Software Works
AI agent software relies on multiple core components working together to deliver seamless functionality and valuable insights.
Input Mechanisms
AI agents are driven by the data they receive. These inputs originate from diverse sources and are crucial for enabling the agents to analyze, predict, and act.
• Data Sources: AI agents process data from structured databases (e.g., SQL), unstructured formats (e.g., emails, PDFs), real-time interactions (e.g., chatbots), and even IoT devices (e.g., smart thermostats or security systems). This versatility allows AI agents to adapt across industries, whether analyzing purchase patterns in retail or monitoring patient vitals in healthcare.
• Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows AI agents to understand and respond to human language. By analyzing text or speech, the agent can interact meaningfully with users. For instance, customer service chatbots employ NLP to interpret user queries and provide relevant responses. Learn more about Natural Language Processing and its applications.
• Real-Time Data Integration: Many AI agents integrate real-time data streams to provide up-to-the-minute insights. For example, in logistics, AI agents track vehicle locations, weather patterns, and traffic conditions to optimize delivery routes instantly.
Processing Unit
The processing unit is the brain of an AI agent, where data inputs are transformed into meaningful actions.
• Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning algorithms form the foundation of decision-making. These algorithms train the AI agent using historical data to predict outcomes, classify information, and recognize patterns. A customer support AI agent, for instance, can predict customer sentiment based on tone and past interactions.
• Knowledge Bases: AI agents rely on built-in knowledge repositories to improve decision-making. Knowledge bases can be static (e.g., product FAQs) or dynamic, learning from every user interaction. They allow AI agents to provide consistent and accurate responses.
• Cognitive Reasoning: Advanced AI agents use reasoning models to simulate human-like thinking. By applying logical rules and past experiences, they make decisions that adapt to unique situations. For example, financial AI agents can recommend investment strategies based on market conditions and user preferences.
Output Mechanisms
The outputs of AI agents are as critical as the inputs. The way an AI agent delivers its responses ensures clarity and usability.
• Actionable Insights: AI agents provide actionable recommendations based on their analysis. For example, an AI-powered marketing agent might suggest optimal posting times for social media content to maximize engagement.
• Automated Task Execution: Many AI agents are programmed to perform actions autonomously. For instance, in HR systems, AI agents can schedule interviews, send follow-ups, or even shortlist candidates based on predefined criteria.
• Interactive Interfaces: Modern AI agents are integrated with user-friendly dashboards, voice assistants, or APIs to facilitate seamless interactions. Platforms like virtual assistants and customer relationship management (CRM) tools offer clear visualizations of the AI’s insights.
Key Technologies Behind AI Agents
AI agents harness a combination of technologies to perform their functions effectively.
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
ANNs mimic the human brain by processing information through interconnected layers of artificial neurons. These networks are particularly effective for tasks like image recognition, language translation, and predictive analytics. For example, AI-powered e-commerce tools use ANNs to recommend products based on user browsing history.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables AI agents to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Chatbots and virtual assistants leverage NLP to enhance conversational experiences. Applications such as IBM Watson Assistant demonstrate how NLP-driven tools deliver accurate and natural interactions.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning involves training AI agents to make decisions through trial and error. By rewarding correct actions, the agent improves over time. This technology is often used in robotics and gaming AI systems.
Generative Models
Generative models, such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), empower AI agents to create original content, such as drafting emails or generating product descriptions. These models are widely used in content creation and customer engagement platforms.
Practical Applications of AI Agent Software
AI agent software is transforming industries by streamlining operations, enhancing decision-making, and delivering personalized experiences. These applications are being implemented in customer service, healthcare, retail, e-commerce, and financial services, with significant real-world case studies highlighting their impact.
Customer Service
AI agents have revolutionized customer service by providing instant, personalized assistance to users. With advanced natural language processing, AI agents handle common inquiries, resolve complaints, and engage in complex problem-solving. Companies like Zendesk utilize AI agents to deliver seamless customer experiences. For example, Zendesk’s AI-powered Answer Bot helps businesses deflect up to 50% of tickets by providing immediate resolutions, reducing wait times, and increasing customer satisfaction
A case study from eBay demonstrates the effectiveness of AI in customer support. The company uses AI agents to handle millions of customer queries, reducing response times dramatically and ensuring a personalized experience. This integration allowed eBay to provide 24/7 support while reducing operational costs and enhancing user engagement.
Healthcare
AI agents play a transformative role in healthcare, aiding patient care and administrative processes. Virtual health assistants, such as those developed by Mayo Clinic, assist patients with symptom checks, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders. These AI tools ensure timely care and reduce the workload on medical staff.
A real-world example is Babylon Health, an AI-powered healthcare app that offers consultations, symptom assessments, and health monitoring. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Babylon Health’s AI triage system proved invaluable by helping users assess symptoms and prioritize care. This minimized unnecessary visits to healthcare facilities and provided vital support to overwhelmed medical systems.
Retail and E-commerce
AI agents are reshaping retail and e-commerce by providing personalized shopping experiences. By analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history, these agents suggest tailored products and services. Companies like Shopify and Amazon leverage AI for recommendations, significantly boosting sales and customer loyalty.
Sephora, a global beauty retailer, integrates AI through its Virtual Artist feature. This tool uses augmented reality to let customers virtually try on makeup, enhancing the shopping experience. Sephora also employs AI agents to provide personalized skincare and beauty recommendations, leading to increased customer satisfaction and higher conversion rates.
Financial Services
The financial sector relies heavily on AI agents for tasks requiring precision and speed. These include fraud detection, credit risk assessment, and portfolio management. AI agents like those from NetSuite analyze transaction patterns in real-time to identify anomalies, safeguarding businesses and customers.
An illustrative case is JPMorgan Chase’s COiN (Contract Intelligence) platform, which uses AI agents to analyze legal documents and extract key information. This tool processes in seconds what would take humans 360,000 hours, significantly increasing efficiency. Similarly, American Express employs AI agents to analyze transactions for fraud, offering real-time alerts to customers and reducing fraudulent activities.
Education and Learning
AI agents are revolutionizing education by offering personalized learning experiences. Platforms like Khan Academy and Coursera use AI agents to recommend courses based on user preferences and learning history. These agents also provide real-time feedback on assignments, helping learners improve quickly.
Carnegie Learning is a notable example, using AI-driven tools to create adaptive math tutoring systems. These systems analyze student performance and adjust lessons in real-time, improving comprehension and engagement. The success of these tools is evident in improved test scores and positive feedback from students and teachers alike.
Logistics and Supply Chain
AI agents streamline logistics by optimizing supply chains and improving delivery processes. Companies like UPS use AI to plan routes, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure timely deliveries. AI agents also manage inventory, predict demand, and automate order fulfillment.
For instance, DHL employs AI agents in its warehouses to optimize storage, automate sorting, and enhance package tracking. These tools enable DHL to handle increased shipment volumes while maintaining high accuracy and efficiency, ensuring customer satisfaction and operational scalability.
Examples of Common AI Agents
AI agent software operates by utilizing algorithms to process data, extract insights from it, and make decisions. Instances of AI agents are evident across several industries such as customer service, healthcare, and finance.
Here are some instances of commonly used AI agents:
- Chatbots: AI-driven chatbots assist in customer service by offering round-the-clock support. They rely on natural language processing (NLP) to comprehend customer inquiries and respond appropriately.
- Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant perform tasks such as setting reminders, sending messages, and making calls through AI capabilities.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents: These agents rely on a representation of the environment to inform their decisions. A self-driving car, for instance, uses an environmental model of the road for decision-making.
- Simple Reflex Agents: These agents respond to the immediate state of their environment without accounting for long-term outcomes. A thermostat, for example, adjusts the temperature based on its current readings.
- Goal-Oriented Agents: Designed with a specific objective, these agents utilize planning and decision-making strategies to achieve their goals. A chess-playing AI, for example, is programmed to aim for victory.
- Reinforcement Learning Agents: By learning through trial and error, these agents improve their actions through rewards or penalties. For instance, a robot learns to pick up objects successfully by receiving positive feedback for correct attempts.
- Generative AI Agents: These agents use generative models to produce new content, such as images, music, or text. For example, generative adversarial networks (GANs) can create AI-generated artwork.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles integrate sensors and AI algorithms to traverse roads and avoid obstacles.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Agents: These agents replicate human actions to automate recurring tasks like data entry or bookkeeping efficiently.
- Predictive Maintenance Agents: These agents apply machine learning to forecast when equipment or machinery will require maintenance.
These examples demonstrate how AI agents serve diverse industries by optimizing efficiency, productivity, and decision-making processes.
Key Features of AI Agent Software
AI agent software transforms complex operations into seamless, efficient processes. It leverages advanced technologies to solve real-world problems while ensuring usability, security, and flexibility. Below, we explore the standout features that define modern AI agent systems and their technical underpinnings.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables AI agents to interpret, understand, and generate human language. By employing advanced models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), NLP bridges the gap between humans and machines.
NLP allows AI agents to process unstructured data such as emails, chats, and documents. For example, customer support bots powered by NLP can resolve user queries with high accuracy. Platforms like Google Cloud Natural Language offer APIs for sentiment analysis, entity extraction, and syntax recognition, enabling businesses to extract actionable insights from text.
Another application of NLP is in healthcare, where agents analyze medical records and provide recommendations. NLP’s ability to recognize complex patterns in natural language data enhances decision-making while reducing processing time for large datasets.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning equips AI agents with the ability to learn from data and improve over time. Using algorithms like decision trees, support vector machines (SVMs), and deep neural networks, AI systems can identify patterns and make predictions without explicit programming.
For instance, in fraud detection, ML algorithms analyze transaction histories to detect unusual activities. Platforms such as AWS Machine Learning provide scalable solutions for training and deploying models that adapt to evolving threats.
In retail, AI agents use ML to personalize recommendations. By analyzing past purchase behavior, agents predict customer preferences and suggest products, driving sales and enhancing customer satisfaction. This dynamic adaptation ensures relevance and efficiency in every interaction.
Integration with Existing Systems
AI agent software integrates seamlessly with existing IT infrastructures, enhancing functionality without requiring complete system overhauls. APIs and middleware solutions allow AI agents to communicate with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and other business software.
For example, integrating an AI agent with Salesforce CRM can automate lead management and improve customer engagement. The AI analyzes past interactions to recommend optimal engagement strategies, boosting conversion rates.
Integration is also crucial in manufacturing, where AI agents work with ERP systems to predict maintenance needs. By analyzing machine data, agents notify operators of potential issues, preventing costly downtime and optimizing resource use.
Automating Repeated Tasks
AI agents excel in automating repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on strategic objectives. By leveraging rule-based algorithms and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), agents can execute high-volume tasks with precision and consistency.
For example, AI-powered email triage systems sort incoming emails based on priority and relevance. In human resources, AI agents streamline processes like resume screening, identifying top candidates based on predefined criteria.
Automation extends to supply chain management, where agents track shipments, generate invoices, and monitor inventory levels. Tools like UiPath enable businesses to deploy scalable automation solutions that adapt to changing requirements.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are foundational to AI agent software. Advanced encryption methods and compliance with global regulations such as GDPR and CCPA ensure sensitive information is safeguarded.
AI agents employ techniques like homomorphic encryption, which allows data to be processed without being decrypted, maintaining confidentiality. Platforms such as Google Cloud Security provide tools for identity management, audit trails, and secure data transfer.
In finance, AI agents use multi-factor authentication and real-time monitoring to prevent unauthorized access. These measures protect not only the integrity of financial transactions but also customer trust, which is vital for any industry.
Customizability
Customizability ensures AI agent software aligns with unique business needs. Modular architectures and configurable workflows allow organizations to tailor AI systems to specific use cases.
For example, businesses can customize chatbots with brand-specific language and tone, creating a cohesive customer experience. Platforms like IBM Watson Assistant enable users to build AI agents with features that reflect organizational goals and values.
Benefits of Using AI Agent Software
Data security measures are crucial when implementing modular systems using composable architecture like AI-powered software agents because they manage large datasets across multiple systems.
In logistics, custom algorithms optimize delivery routes based on specific constraints like delivery time windows and fuel efficiency. This adaptability ensures that AI solutions remain effective even as operational requirements evolve.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Modular systems supported by composability significantly enhance efficiency by automating repetitive tasks while minimizing human errors. Composability refers to designing systems with modular components that can function independently or collectively. This design approach allows organizations to adapt and reconfigure processes without rebuilding entire systems, ensuring flexibility and resilience.
For instance, in logistics, AI-driven modular systems automate inventory tracking, shipment scheduling, and invoice generation. These systems use predictive algorithms to identify potential delays and optimize delivery routes in real-time, reducing overhead costs and improving operational speed. A case study by McKinsey revealed that automation in supply chain management could reduce costs by 20-30% while increasing accuracy and efficiency (McKinsey Digital).
In healthcare, composable AI modules enable faster patient diagnostics by automating data analysis from medical records, imaging systems, and wearable devices. By reducing manual data processing, doctors can focus on patient care, improving outcomes and reducing wait times. The integration of composable systems into Electronic Health Records (EHR) has revolutionized efficiency, ensuring scalable and error-free operations.
Enhanced Customer Experiences
AI systems equipped with advanced analytics tools empower organizations to make data-driven decisions across diverse sectors. These systems process vast datasets, uncovering patterns and trends that humans might overlook. This capability ensures that businesses can adapt swiftly to market changes and optimize strategies for better outcomes.
For example, AI-powered decision-making tools in finance analyze market trends, evaluate risks, and forecast economic conditions with high precision. Financial firms use platforms like Tableau to visualize complex datasets, enabling informed investment strategies (Tableau Official). Similarly, in agriculture, AI-driven systems assess soil health, weather patterns, and crop yields, guiding farmers toward optimal resource allocation.
AI-enhanced decision-making tools also improve adaptability in manufacturing. Predictive maintenance systems analyze machine data to predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime and extending equipment life. This proactive approach increases productivity and ensures continuous operations.
Boost Productivity
Collaborative AI agents significantly boost productivity by streamlining workflows and reducing the complexity of tasks. Integrating multiple intelligent agents ensures seamless communication between systems, enabling end-to-end automation. The advent of No Code tools simplifies deploying such agents, allowing non-technical users to build and manage workflows efficiently.
For instance, in customer service, AI agents like chatbots and virtual assistants handle inquiries, route tickets, and provide real-time solutions. This not only reduces response times but also frees up human agents to focus on complex issues. A study by Gartner predicts that chatbots will handle 85% of customer interactions in the near future (Gartner).
In education, collaborative AI systems facilitate personalized learning experiences by analyzing student performance and providing tailored content. Platforms like Khan Academy use AI to adapt lesson plans dynamically, ensuring that students learn at their own pace. These advancements simplify operations and enhance user satisfaction across industries.
Scalability for growing businesses
Scalability is a crucial feature for growing organizations, and AI-enabled automation ensures seamless expansion. By automating repetitive processes, businesses can focus on strategic goals without being hindered by operational bottlenecks. Scalable AI solutions, such as virtual assistants, enhance customer support and strengthen brand perception.
For example, e-commerce companies use AI to automate inventory management, personalized recommendations, and order processing. Amazon’s AI-driven systems track user behavior and suggest products, ensuring a smooth shopping experience. This personalization enhances customer loyalty and boosts sales (Amazon AI).
In human resources, AI tools streamline recruitment by analyzing resumes, scheduling interviews, and even onboarding new employees. As businesses grow, these automated processes scale effortlessly, reducing administrative workloads and improving efficiency.
Build Custom Solutions
Customizable AI systems offer organizations the flexibility to create solutions that align with specific business needs. These tailored applications ensure that operations are efficient and responsive to unique challenges. Customization enables organizations to integrate industry-specific requirements, enhancing service delivery and overall performance.
For instance, in retail, businesses use customized AI algorithms to analyze buying trends and predict inventory demands. By tailoring solutions to customer behavior, retailers minimize stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory management. Platforms like IBM Watson offer tools to develop industry-specific AI solutions, ensuring that businesses remain competitive (IBM Watson).
In healthcare, custom AI systems address unique operational requirements, such as patient record management and telemedicine. Hospitals use AI-driven platforms to develop diagnostic tools that align with their resources and workflows. These solutions ensure that services are delivered efficiently, improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
By leveraging the flexibility of customizable systems, organizations can develop tools that drive growth, enhance productivity, and adapt to changing market demands.
Common Use Cases of AI Agents
Customer Support: AI-powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have transformed customer support, providing immediate and efficient responses to user queries while reducing operational costs. These tools simulate human-like interactions using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) to understand, process, and respond to user inquiries.
How They Work
Chatbots are programmed to handle repetitive questions, such as tracking orders or resetting passwords. Virtual assistants, on the other hand, are more sophisticated, capable of managing complex tasks like booking appointments or troubleshooting issues. Both rely on AI algorithms to learn from interactions and improve over time.
Real-Life Case Study: Zendesk’s Chatbots
Zendesk has integrated AI chatbots into its customer service platforms, helping businesses streamline interactions. A notable example is a retail client that deployed Zendesk’s AI chatbot to manage holiday season inquiries. The chatbot successfully handled 70% of queries autonomously, reducing response times by 60% and boosting customer satisfaction (Zendesk Official).
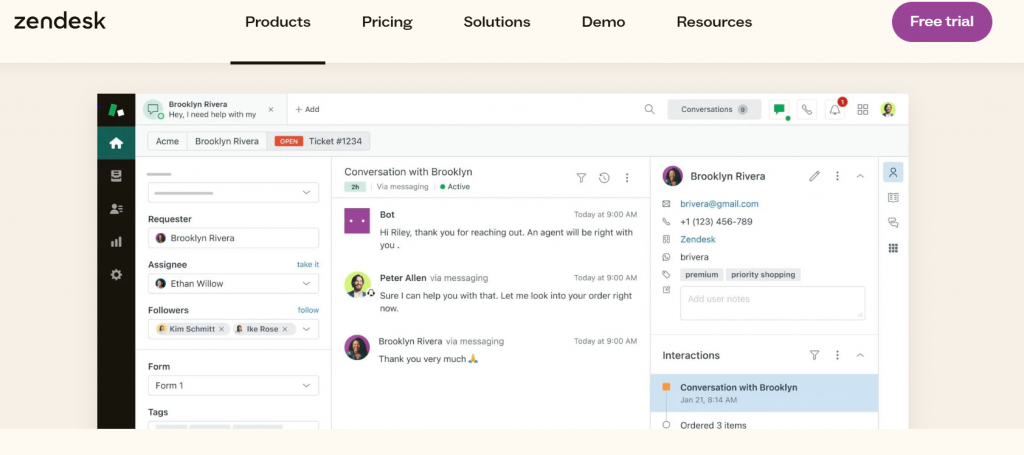
Why It Matters
These AI tools enhance user experience by providing 24/7 support, minimizing wait times. They also reduce the burden on human agents, allowing them to focus on complex issues. In addition, businesses benefit from lower costs and increased scalability, as AI-powered solutions can handle millions of interactions without additional resources.
E-Commerce: Personalization, Inventory Management, and Sales Predictions
AI is revolutionizing e-commerce by offering personalized shopping experiences, optimizing inventory management, and predicting sales trends. These applications ensure seamless operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
How They Work
AI algorithms analyze customer behavior, purchase history, and browsing patterns to offer tailored product recommendations. Inventory management systems use predictive analytics to forecast demand, ensuring optimal stock levels. Similarly, sales prediction tools analyze market trends and customer preferences to identify future opportunities.
Real-Life Case Study: Amazon’s Recommendation Engine
Amazon’s AI-powered recommendation engine generates 35% of the company’s revenue by personalizing product suggestions based on user behavior (Forbes). For example, if a user purchases a camera, Amazon suggests compatible accessories like lenses or tripods, enhancing the shopping experience.
Why It Matters
Personalization increases conversion rates and customer loyalty. Predictive inventory management minimizes stockouts and overstocking, reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency. These AI-driven solutions empower e-commerce businesses to deliver value while staying competitive.
HR: Recruitment, Onboarding, and Employee Engagement
AI has redefined Human Resources (HR) processes, automating recruitment, onboarding, and employee engagement. These applications save time, reduce biases, and ensure a positive workplace experience.
How They Work
Recruitment tools use AI to scan resumes, match candidates to job descriptions, and shortlist top talent. Onboarding platforms automate paperwork, schedule training sessions, and introduce new hires to company policies. For ongoing engagement, AI systems monitor employee sentiment and suggest personalized wellness programs.
Real-Life Case Study: Unilever’s AI-Driven Recruitment
Unilever adopted AI to screen candidates, replacing traditional methods with gamified assessments and video interviews analyzed by AI. This approach reduced hiring time by 75% and increased the diversity of new hires (Harvard Business Review).
Why It Matters
AI enhances efficiency in hiring and onboarding, ensuring that businesses find the right talent quickly. By automating repetitive tasks, HR teams can focus on strategic initiatives. AI-driven engagement tools also foster a happier, more productive workforce.
Healthcare – Scheduling, Patient Communication, and Record Management
AI is transforming healthcare by streamlining administrative tasks, improving patient communication, and managing medical records securely and efficiently.
How They Work
AI tools schedule appointments based on patient preferences and doctor availability. Chatbots answer common medical questions and remind patients about medications or upcoming appointments. Record management systems digitize and organize patient data, enabling easy access for healthcare providers.
Real-Life Case Study: Mayo Clinic’s AI Integration
Mayo Clinic uses AI to manage patient scheduling and predict appointment no-shows, optimizing resource allocation. This system reduced missed appointments by 30%, improving operational efficiency and patient care (Mayo Clinic Proceedings).
Why It Matters
AI in healthcare reduces administrative burdens, allowing providers to focus on patient care. Improved communication and accurate record-keeping enhance the overall patient experience and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
Marketing and Sales: Lead Generation, Personalization, and Campaign Automation
AI is reshaping marketing and sales by automating lead generation, delivering personalized content, and streamlining campaign management. These tools help businesses connect with their audience more effectively.
How They Work
AI systems analyze user data to identify potential leads and qualify them based on predefined criteria. Content personalization tools create dynamic ads, emails, or landing pages tailored to individual preferences. Campaign automation platforms optimize timing and delivery, ensuring maximum impact.
Real-Life Case Study: HubSpot’s AI-Driven Marketing Automation
HubSpot leverages AI to personalize email campaigns and score leads based on their likelihood to convert. A software company using HubSpot reported a 50% increase in qualified leads and a 30% boost in sales conversions (HubSpot Official).
Why It Matters
AI-driven marketing tools ensure that cmpaigns reach the right audience at the right time, maximizing ROI. Automation simplifies complex workflows, allowing teams to focus on creative strategies. Enhanced personalization fosters stronger customer relationships and drives revenue growth.
Challenges and Limitations
AI agent software faces difficulties despite its promising benefits; Implementing modular designs can address some of these challenges.
Here are some common issues:
- Modular design requires cautious adoption because complex integration demands thorough planning.
- Initial costs can be a barrier for small businesses since high upfront expenses discourage adoption among cost-conscious companies.
- Data privacy concerns grow as reliance on quality training data exposes sensitive data to potential risks.
- The intricate nature of the technology can make user adaptation difficult as integration challenges affect usability.
- Selecting appropriate vendors can be challenging as numerous providers with competing options create confusion for buyers.
- AI regulations create hurdles since unclear laws complicate broader adoption by organizations.
- Integrating multiple modules requires advanced expertise since various components need specific implementation processes.
- Representing business goals mathematically introduces inherent challenges as converting objectives into algorithms is a demanding task.
- Training algorithms demand expensive computational resources since processing power requirements lead to significant upfront investments.
- Maintenance involves costly updates because regular revisions incur substantial ongoing expenses.
Implementation Complexity
Deploying AI agent software can be a daunting task due to the technical requirements, infrastructure needs, and expertise involved. Companies often face challenges in integrating AI into their existing systems, requiring careful planning and execution.
The Complexity of Integration
AI agent software must work seamlessly with legacy systems, cloud platforms, and other technologies in place. The process involves configuring APIs, ensuring compatibility, and handling potential disruptions during the migration. Companies without scalable IT infrastructure may struggle to accommodate the computational demands of AI.
Need for Skilled Workforce
The implementation process requires AI experts, data scientists, and IT professionals who understand the intricacies of machine learning algorithms, data processing pipelines, and system architecture. A lack of skilled personnel can lead to delays or suboptimal performance, hindering the success of AI projects.
When IBM Watson was introduced to assist with oncology treatment recommendations, many healthcare organizations found implementation complex. Integrating Watson with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) required extensive technical customization and training for medical staff. Despite these challenges, successful deployments led to improved diagnostic capabilities (source).
Addressing the Challenge
To mitigate implementation complexity, businesses can adopt a phased approach, starting with pilot projects before scaling up. Leveraging cloud-based AI solutions can also reduce the burden of on-premises infrastructure.
High Initial Costs
The cost of adopting AI agent software can be significant, making it a barrier for small and medium-sized businesses. Expenses include software licensing, hardware upgrades, and training programs, all of which can add up quickly.
Cost of AI Tools and Infrastructure
AI software often comes with a high price tag, particularly for advanced platforms offering sophisticated features like natural language processing and predictive analytics. Additionally, the computational resources required for AI, such as GPUs and cloud computing services, further increase costs.
Ongoing Maintenance and Upgrades
AI systems are not static; they require continuous updates to adapt to new data and maintain optimal performance. Maintenance costs, including system monitoring and retraining models, add to the financial burden.
Tesla’s self-driving AI is an example of high upfront investment. The company spends billions on developing neural networks, processing data from millions of vehicles, and refining algorithms. These investments, while substantial, have positioned Tesla as a leader in autonomous vehicle technology (source).
Addressing the Challenge
Companies can explore cost-sharing models like partnerships or subscriptions to reduce upfront expenses. Open-source AI frameworks, such as TensorFlow or PyTorch, offer alternatives for businesses looking to minimize licensing costs.
Data Privacy Concerns
AI agent software relies heavily on data, raising significant concerns about privacy and compliance. Mishandling sensitive information can lead to legal repercussions and loss of customer trust.
The Importance of Data Security
AI systems process vast amounts of personal and organizational data, including customer records, financial transactions, and medical histories. Protecting this data from breaches is crucial to maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
Compliance with Regulations
Businesses must navigate complex regulatory landscapes, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California, which mandate strict data handling and reporting requirements. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
In 2018, Facebook faced scrutiny for its involvement in the Cambridge Analytica scandal, where user data was misused to influence political campaigns. This highlighted the need for stringent data governance in AI applications (source).
Addressing the Challenge
Adopting encryption, anonymization techniques, and secure data storage protocols can mitigate privacy risks. Regular audits and compliance checks ensure adherence to regulations.
Dependence on Quality Training Data
The performance of AI agent software hinges on the quality of data used for training. Inaccurate, incomplete, or biased datasets can lead to unreliable predictions and suboptimal outcomes.
The Impact of Data Quality
AI algorithms learn patterns from historical data. If the training data is flawed, the resulting model will inherit these issues, leading to inaccurate or unfair decisions. For instance, biased data in recruitment software can perpetuate discrimination.
Challenges of Data Collection
Collecting high-quality data is time-consuming and resource intensive. Businesses must ensure that the data is representative of diverse scenarios to avoid skewed results.
Amazon’s AI-powered recruitment tool was found to favor male candidates due to biased training data that reflected historical hiring practices. This led to the discontinuation of the tool and underscored the importance of balanced datasets (source).
Addressing the Challenge
Organizations should invest in data curation and preprocessing to ensure quality. Techniques like data augmentation and synthetic data generation can enhance dataset diversity, improving model reliability.
How to Choose the Right AI Agent Software
Choosing the right software requires a structured approach that ensures compatibility, scalability, and efficiency.
Below, we break down a comprehensive guide to help you select the perfect solution for your needs.
Define Objectives and Use Cases
The first step in selecting the right AI agent software is to define clear objectives and identify the specific use cases where the software will be implemented. This sets the foundation for evaluating potential solutions.
Identify Core Goals
Determine whether you need the software for automating repetitive tasks, enhancing customer support, or analyzing complex data. For example, a retail business may want to use AI agents to automate inventory management and improve customer service.
Amazon uses AI-driven agents to streamline logistics, handle customer queries, and predict inventory needs. These tools have enabled Amazon to provide faster delivery times and improved customer satisfaction.
By clearly understanding what you want to achieve, you can focus on solutions designed to address those specific challenges.
Evaluate Features
AI agent software comes with a diverse range of features. Understanding which features align with your goals ensures you invest in a tool that meets your requirements. Look for essential capabilities such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) for conversational AI, machine learning algorithms for adaptive behavior, and integration capabilities for seamless connectivity with existing tools like CRMs or ERP systems.
Companies like Zendesk use AI-powered agents that combine NLP and real-time data analytics to deliver efficient customer support. These agents can understand customer intent and provide accurate responses, improving the overall experience.
Ensure the software supports automation to handle repetitive tasks, such as ticket resolution or order processing, freeing up human employees for more complex tasks.
Assess Scalability
Scalability is crucial for businesses expecting growth or increased operational demands. AI agent software should not only meet your current needs but also support expansion. Check if the software can handle increased data volumes, multiple users, or additional processes as your business grows. Cloud-based solutions often offer greater scalability than on-premises systems.
Netflix uses AI agents to recommend content based on user behavior. As Netflix’s user base grew, its AI system scaled to handle billions of data points, ensuring personalized recommendations for every subscriber.
For teams, ensure the software supports role-based permissions and collaborative features.
Analyze Usability
Ease of use is a critical factor when adopting AI agent software. Complex tools can lead to poor adoption rates and inefficiencies. Look for software with a user-friendly interface, clear navigation, and easy setup. Tools with visual workflows often simplify training for non-technical users.
Shopify integrates AI chatbots that require minimal setup and provide easy customization options for small businesses.
Check if the vendor provides tutorials, live support, and detailed documentation to help users get started quickly.
Consider Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are critical in today’s digital landscape. AI agent software must protect sensitive information while complying with regulations.
Ensure the software uses strong encryption to safeguard data both in transit and at rest. Look for certifications like ISO 27001. Verify that the software adheres to data privacy laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
Healthcare providers using IBM Watson ensure patient data privacy by leveraging secure AI systems compliant with HIPAA standards.
Check Vendor Support
Robust customer support ensures smooth implementation and ongoing performance of AI agent software. Choose vendors offering 24/7 support through multiple channels such as email, chat, and phone. Access to a dedicated account manager can be beneficial for enterprise solutions.
Salesforce provides extensive support, including training sessions and a knowledge base, ensuring customers can leverage the full potential of its AI-powered tools.
Look for vendors with comprehensive guides, video tutorials, and community forums.
Compare Pricing Models
The cost of AI agent software varies depending on features, scalability, and deployment model. Understanding pricing structures helps you make an informed decision.
Many vendors offer tiered plans based on usage, making it easier for small businesses to start and scale as needed. For large enterprises, vendors often provide tailored pricing based on unique requirements.
Adobe’s AI-driven solutions offer flexible pricing for businesses of all sizes, from startups to global enterprises.
Test Performance with a Pilot Project
Before full implementation, a pilot project allows you to evaluate the software’s capabilities in real-world scenarios. Assess how quickly the software can be deployed and integrated with your systems.
Track key metrics such as response time, accuracy, and user satisfaction during the pilot phase.
A logistics company tested AI routing software on a single delivery route before rolling it out nationwide, ensuring compatibility and effectiveness.
Evaluate Long-Term Viability
Choose software that aligns with your future needs and industry trends. Research customer reviews and case studies to gauge the vendor’s reliability.
Ensure the software is regularly updated with new features and improvements.
Tesla’s AI systems continue to evolve with regular updates, ensuring the company remains a leader in autonomous vehicle technology.
Future Trends in AI Agent Software
AI agent software is evolving rapidly, and its future trends reflect transformative possibilities across industries. Modular systems, generative AI, and hyper-personalization are shaping the way businesses utilize these tools for enhanced productivity and decision-making. Below, we explore these trends with real-world examples and expert insights.
Generative AI and Autonomous Agents
Generative AI is enabling AI agents to handle complex tasks with minimal human intervention. These agents can generate innovative solutions by leveraging learned patterns from vast datasets, making them indispensable for industries requiring creativity and efficiency.
Odin AI integrates generative capabilities to automate repetitive tasks, allowing businesses to focus on strategic goals. For example, companies in e-commerce use Odin AI to create personalized shopping experiences, reducing cart abandonment rates.
Platforms like IBM Watson Assistant demonstrate the power of generative AI by providing intelligent customer support that evolves based on user interactions, minimizing the need for manual adjustments.
These systems are advancing autonomous decision-making, as seen in logistics, where AI agents optimize delivery routes without human intervention, saving time and fuel.
Hyper-Personalization
Hyper-personalization leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning to deliver tailored experiences to each user. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and demographics, AI agents create unique interactions that enhance engagement and satisfaction.
Spotify uses AI-driven hyper-personalization to curate playlists based on individual listening habits, achieving higher user retention rates. This approach transforms customer interactions into deeply personalized experiences.
Tools like Google Analytics integrate predictive analytics to understand customer journeys, enabling businesses to offer hyper-specific solutions. For instance, retail companies use these insights to recommend products with a high likelihood of purchase.
This strategy drives increased customer loyalty and revenue growth, as businesses deliver what users want before they even know they need it.
Scalable and Modular Systems
Modular systems offer adaptability and scalability, making it easier for businesses to implement AI solutions that grow with their needs. These systems allow individual components to work together seamlessly, enabling efficient task sharing and resource allocation.
Tesla employs modular AI systems in its autonomous vehicles, where different modules handle navigation, object detection, and decision-making. This setup allows Tesla to scale and update individual features without overhauling the entire system.
Compound AI frameworks like those discussed by OpenAI highlight the potential of modular systems to enhance flexibility and efficiency in AI implementations.
These frameworks support businesses in managing increasing data volumes and expanding operations without compromising performance.
Predictions for AI Agent Adoption
The adoption of AI agents is expected to accelerate across industries, driven by their ability to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. Healthcare, finance, and customer service are leading this transformation.
Healthcare providers like Mayo Clinic use AI agents to streamline patient scheduling and manage medical records, reducing administrative burdens and improving patient care.
According to Gartner, 70% of companies will deploy AI agents by 2028, with significant savings in operational costs and improved decision-making based on AI-generated insights.
AI agents will take over routine tasks, allowing humans to focus on strategic initiatives and creative problem-solving.
This widespread adoption signifies a shift toward AI-enhanced workflows, where humans and intelligent systems collaborate to achieve greater outcomes.
Conclusion
The adoption of AI agent software is a game-changing step for businesses striving for innovation and efficiency. Leaders like Dr. Jensen and Dr. Lee emphasize the potential of modular systems and ethical AI practices in driving success.
By leveraging tools like Mosaic AI Gateway and Odin AI, organizations can transform their workflows, deliver better customer experiences, and achieve sustainable growth.
Frequently asked questions
What is AI agent software – and how does it work?
AI agent software is a program that uses artificial intelligence to perform tasks, like answering questions, or helping with jobs. It works by using special codes, and data to make decisions.
What are the benefits of using AI agent software – in my business?
The benefits are many, including saving time, and money… it can also help with customer service, by answering questions, and solving problems quickly.
What are some use cases for AI agent software – in different industries?
AI agent software can be used in many industries, like healthcare, finance, and retail. It can help with tasks, like booking appointments, or processing payments.
How do I choose the right AI agent software – for my needs?
To choose the right AI agent software, you need to think about what you want it to do… consider what features you need, like natural language processing, or machine learning – and then pick the one that best fits your needs.




